Heart problems can often affect your eyes and have links to an increased risk of developing some eye disorders. Cardiovascular disease is a term used for conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels all over the body, including the ones in the eye — which supply blood to the retina. The risk of having heart problems and cardiovascular diseases can stem from conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol. An eye examination can also detect underlying coronary heart disease (CHD), which is the leading cause of heart attacks. Here are five ways you can detect through eyes whether you have a higher chance of heart attack or not.
Blurry vision and chest pain
Medical conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure including heart attack can damage the blood vessels in the eyes and result in blurred or altered vision. They can reduce blood supply and also starve the eyes of oxygen, affecting vision. Visual disturbances like blurred vision that occur with chest pain can indicate high blood pressure and a heart attack.
Bloodshot eyes
High blood pressure can cause bloodshot eyes which is also a condition called hypertensive retinopathy. The person can have tiny blood vessels in the white area of the eye visible and can burst making them look bloodshot. High Blood pressure can also cause blood clots which damage the retina, vision loss, visual changes and headaches.
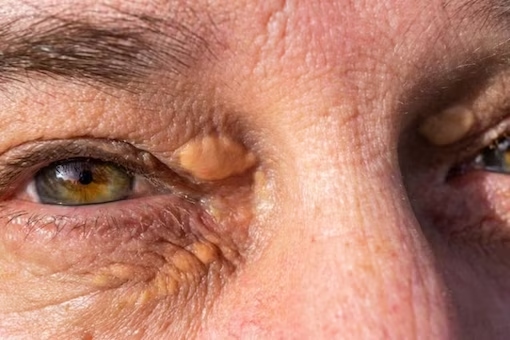
Yellowish deposit under eyes
If you ever notice a yellowish deposit on the skin right under your eyes, then you should get your heart checked. This can happen due to an underlying heart condition which can cause a heart attack later.
Shrinking of retina
When someone has atherosclerotic heart disease, macular degeneration starts happening in the eyes. In simple terms, the retina starts to dry up, which can also lead to complete vision loss.
Cataract
Some studies have also proven that cataracts can also occur in the eyes due to heart disease. This is also one of the reasons why those who undergo cataract surgery have a higher risk of death from heart attack or stroke.